The Role of Autonomous Vehicles in Future Mobility
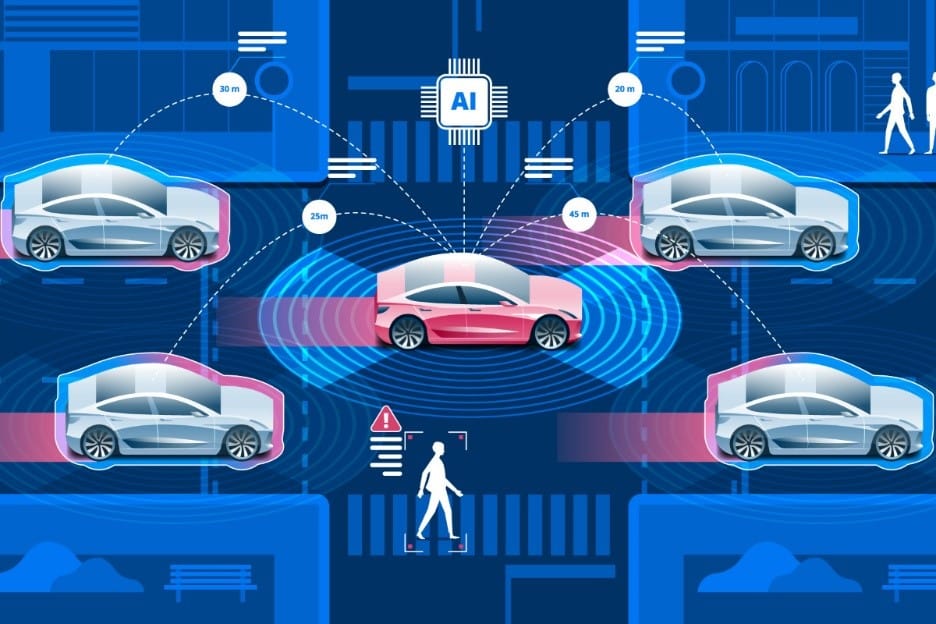
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are set to transform the future of mobility by providing safer, more efficient, and convenient transportation. As technology advances, AVs promise to address various challenges associated with traditional transportation, such as traffic congestion, road accidents, and environmental impact. The development of autonomous driving technology is paving the way for new business models, urban planning, and mobility solutions that can shape the future of how people and goods move.
1. Enhancing Road Safety
One of the most significant benefits of autonomous vehicles is their potential to improve road safety. Human error is a leading cause of traffic accidents, accounting for nearly 90% of crashes worldwide. AVs use advanced sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor the environment, detect obstacles, and make decisions in real time, reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Autonomous driving systems can maintain a safe distance from other vehicles, adhere to speed limits, and react faster to sudden changes in traffic conditions. Additionally, they are not prone to distractions, fatigue, or impaired driving, making them a safer alternative to human drivers.
2. Reducing Traffic Congestion
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce traffic congestion by optimizing traffic flow and decreasing the need for human intervention. AVs can communicate with each other and traffic management systems to coordinate movements, adjust speeds, and avoid bottlenecks. This level of coordination can help prevent traffic jams and improve the overall efficiency of road networks.
Moreover, AVs can promote the use of shared mobility services, such as robo-taxis and autonomous shuttles, reducing the number of private vehicles on the road. This shift toward shared transportation can lead to a more efficient use of road space and help alleviate urban congestion.
3. Enabling New Mobility Services
The introduction of autonomous vehicles is opening up new possibilities for mobility services. Autonomous ride-hailing services, delivery robots, and autonomous freight transport are emerging as potential applications of AV technology. For instance, companies like Waymo and Cruise are already testing autonomous ride-sharing services in select cities, allowing passengers to travel in self-driving cars.
In logistics, autonomous trucks can revolutionize the transportation of goods by providing 24/7 operations, reducing delivery times, and lowering costs. Autonomous last-mile delivery robots are also being developed to bring packages directly to customers’ doorsteps, further enhancing convenience and efficiency.
4. Improving Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles can play a vital role in improving accessibility for individuals who are unable to drive due to age, disability, or other limitations. Self-driving cars can provide an independent mode of transportation for elderly and disabled individuals, enabling them to travel more freely and access essential services.
AVs can also improve access to public transportation by providing first- and last-mile connectivity. Autonomous shuttles can transport passengers from their homes to transit stations, making public transportation more accessible and convenient, especially in suburban and rural areas.
5. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce the environmental impact of transportation by promoting fuel efficiency and the use of electric vehicles (EVs). AVs can optimize driving patterns, such as acceleration, braking, and route selection, to minimize energy consumption. When combined with electric powertrains, autonomous driving can further decrease greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
Additionally, the widespread adoption of shared autonomous mobility services can reduce the need for private car ownership, resulting in fewer vehicles on the road and lower resource consumption. This shift can contribute to more sustainable urban development and help cities meet their environmental goals.
Challenges of Autonomous Vehicles
Despite their potential benefits, autonomous vehicles face several challenges that need to be addressed before they can be widely adopted:
- Technological Limitations: While AV technology has made significant progress, there are still limitations in handling complex driving scenarios, such as adverse weather conditions, road construction, and unpredictable pedestrian behavior.
- Regulatory and Legal Issues: The widespread deployment of AVs requires regulatory frameworks that address liability, insurance, and safety standards. Policymakers need to establish clear guidelines for testing and deploying AV technology on public roads.
- Public Acceptance and Trust: Gaining public trust in autonomous vehicles is essential for their widespread adoption. Concerns about safety, data privacy, and job displacement need to be addressed to build confidence in the technology.
- Cost and Infrastructure Requirements: Developing and deploying autonomous vehicles can be expensive, and the necessary infrastructure, such as smart traffic signals and connected roadways, may require significant investment.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
The future of autonomous vehicles will likely unfold in stages, with different levels of autonomy being adopted incrementally:
- Level 2 and 3 Automation: In the short term, vehicles with partial automation (Level 2) and conditional automation (Level 3) will become more common. These vehicles can assist with tasks such as lane-keeping and adaptive cruise control but still require human oversight.
- Level 4 and 5 Automation: In the long term, fully autonomous vehicles (Level 4 and Level 5) that do not require human intervention are expected to emerge. These vehicles will be capable of operating in most driving conditions without human input, potentially transforming public transportation, logistics, and personal mobility.
The pace of adoption will vary by region, with urban areas likely to see faster integration due to higher demand for shared mobility services and supportive infrastructure.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to reshape the future of mobility by enhancing road safety, reducing congestion, enabling new mobility services, improving accessibility, and promoting sustainability. While there are challenges to overcome, such as technological limitations, regulatory issues, and public acceptance, the benefits of autonomous driving technology make it a promising solution for future transportation needs. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, autonomous vehicles will play a key role in shaping a more efficient, accessible, and sustainable mobility landscape.




